The New Frontier in Pulmonary Embolism Treatment: A Critical Look at the TendviaTM System
The evolution of modern cardiovascular interventions has brought us to a stage where even the most intimidating and nerve‐racking challenges in healthcare, such as high‐risk pulmonary embolism, can now be met with innovative solutions. In this opinion editorial, we take a closer look at the recent clinical study on the TendviaTM pulmonary artery stent thrombectomy system, an approach that promises relief for patients facing intermediate-high and high-risk acute pulmonary embolism. Here, we digest the study’s fine points, discuss its key outcomes, and explore how this emerging technology could prove critical in managing these serious conditions.
In the world of cardiovascular medicine, finding your way through the tricky parts of patient management is essential. As new strategies arise, it is important to consider not only the clinical data but also what these findings mean for physicians, patients, and the broader healthcare community. This editorial aims to piece together the evidence from the study, while also sharing some thoughts on the future potential of mechanical thrombectomy techniques.
Understanding High-Risk Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism, especially in its intermediate-high and high-risk forms, is a condition loaded with problems that demand timely and effective intervention. These life-threatening blocks in the pulmonary arteries can lead to dangerous increases in pulmonary artery pressure, significant strain on the right side of the heart, and ultimately, heart failure. When you consider the delicate balance required in cardiovascular systems, it becomes clear why working through these challenges is so crucial.
While traditional management of pulmonary embolism has heavily relied on anticoagulant therapy and, in severe cases, systemic thrombolysis, the rise of minimally invasive techniques promises more targeted care. There are several key indicators used in managing these patients:
- Pulmonary artery pressure: A critical measure that, when elevated, can indicate the severity of embolic obstruction.
- Right ventricular (RV) function: Evaluated by the ratio of right ventricular diameter to left ventricular diameter (RV/LV), offering insight into the strain imposed by the embolism.
- Biochemical markers: Substances like troponin, D-dimer, and NT-BNP can signal myocardial injury, clot formation, and cardiac strain.
Understanding these parameters is not only essential for diagnosis but also for monitoring the response to treatment. Even the tiniest twists and turns in these readings can carry significant implications for patient care.
Mechanical Thrombectomy: Changing the Game
The investigation into the TendviaTM pulmonary artery stent thrombectomy system provides compelling evidence that mechanical thrombectomy could redefine treatment strategies for high-risk pulmonary embolism. Unlike traditional interventions, percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy (PMT) offers a means to physically remove the clot, rather than relying only on chemical dissolution. This direct approach comes with several potential advantages:
- Immediate reduction in pulmonary artery pressure: The study demonstrated that pressure levels were significantly lower after the procedure.
- Rapid symptom relief: Patients experienced marked alleviation of chest tightness, pain, and dyspnea, which are often nerve-racking conditions to manage.
- Minimally invasive nature: The PMT procedure minimizes the need for open surgery, reducing the risk of infection and other complications.
These benefits underscore why such innovative techniques are being welcomed both by practitioners and patients. However, it is important to note that while mechanical thrombectomy offers promise, careful patient selection and meticulous management are required to ensure optimal outcomes.
Evaluating the Clinical Efficacy of the TendviaTM System
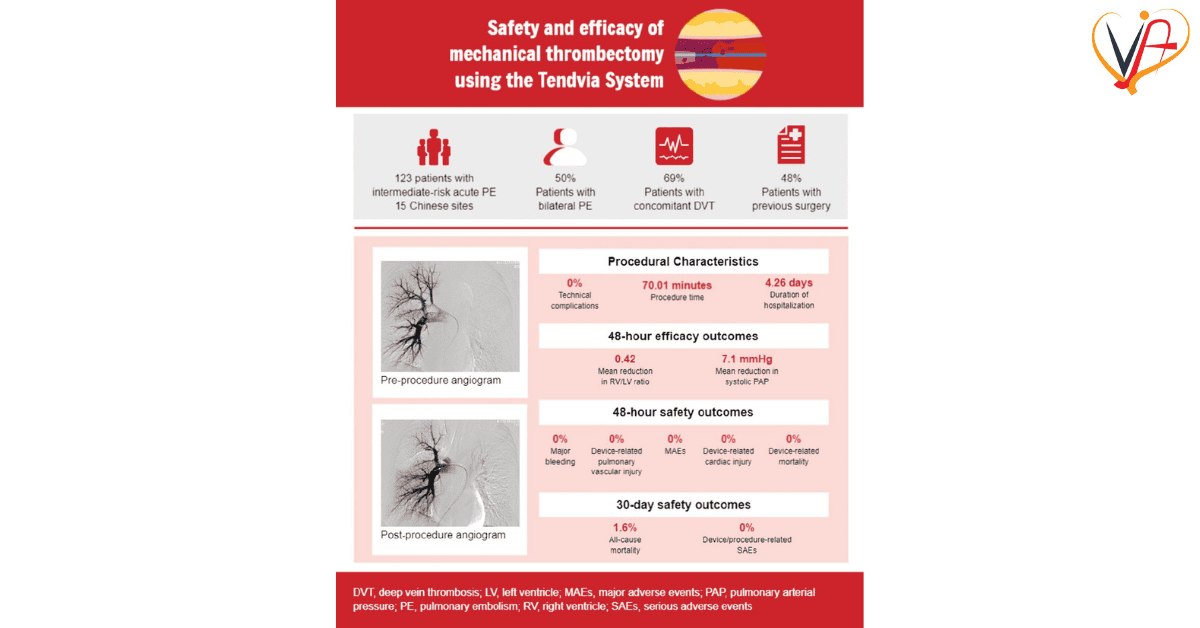
The study in focus evaluated 15 consecutive patients with acute pulmonary embolism, carefully monitored over several weeks at Northeast Yunnan Central Hospital. The patient cohort, which included both male and female subjects with a mean age in the mid-sixties, presented a diverse cross-section of the affected population. Despite the intimidating complexity of managing such patients, the results were encouraging. All cases demonstrated a clear improvement in pulmonary hemodynamics and heart function.
Key observations from the study include:
- Significant reduction in pulmonary artery pressure: This was a major indicator that the procedure was effective in removing the clot burden.
- Diagnostic improvements in echocardiographic RV/LV ratios: Such changes are important because they reflect the heart’s ability to recover from blood vessel blockages.
- Biochemical marker trends: The decrease in levels of troponin, D-dimer, and NT-BNP post-procedure provides additional evidence of the therapy’s efficacy.
These nitty-gritty details help build a case for the stent thrombectomy system as a reliable tool in the arsenal against high-risk pulmonary embolism. Although the sample size is relatively small, the consistency of the results across multiple parameters suggests that there is significant promise for broader application.
Perceived Safety and Effectiveness: A Closer Look
One of the major considerations when adopting any new medical technique is safety. The tendency for innovative therapies to be accompanied by unforeseen complications is a common worry among clinicians. That said, in the study we are examining, no surgical mortality was reported, and procedural complications were minimal. This safety profile is a crucial factor when considering treatment options for patients who are already in a fragile state.
A more detailed look at the procedure’s safety aspects reveals several points worthy of further discussion:
- Short intervention time: The techniques involved allow for rapid clot removal, reducing the time the patient is exposed to high-risk conditions.
- Low procedural risk: The minimally invasive nature means that the risks associated with open surgery, such as significant blood loss or extended recovery times, are largely avoided.
- Minimal post-procedural complications: The study reported no immediate mortalities and only a low incidence of minor complications, which is very reassuring, especially in a critical care setting.
These positive safety indicators are complemented by improvements in patient outcomes. The reassuring reduction in pulmonary artery pressure and the normalization of RV function underscore the procedure’s effectiveness and highlight how advanced interventions can turn overwhelming clinical scenarios into manageable ones.
Comparative Analysis: Mechanical Thrombectomy Versus Traditional Therapies
It is worthwhile to compare the approach of mechanical thrombectomy with traditional treatments such as systemic thrombolysis. Both strategies have their advantages and particular areas of application. While systemic thrombolysis acts by dissolving clots chemically over time, mechanical thrombectomy physically clears the clot almost immediately. This direct removal can be especially useful in patients where time is of the essence. Let’s look at a short comparison:
| Treatment Aspect | Systemic Thrombolysis | Mechanical Thrombectomy (TendviaTM) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Chemical dissolution of clots | Physical extraction of clots |
| Speed of Action | Slower, dependent on clot dissolution | Rapid, with immediate reduction in obstructive burden |
| Risk Profile | Higher bleeding risk, particularly intracranial hemorrhage | Lower bleeding risk, minimally invasive |
| Patient Suitability | Often used as first-line treatment in less severe cases | Ideal for high-risk cases where time is critical |
This table highlights the strengths and limitations of each modality. While systemic thrombolysis remains an important tool, the ability to perform a targeted intervention with devices like the TendviaTM system may shift the balance in favor of mechanical thrombectomy in certain high-risk scenarios. Importantly, the potential benefits in reducing hospital stay and improving immediate outcomes make this tool a must-have consideration for contemporary cardiovascular care.
Reflecting on the Study’s Real-World Implications
A key advantage of this study is its real-world setting. Conducted at a trusted cardiovascular surgery center in Zhaotong, China, the research reflects everyday clinical scenarios rather than idealized research conditions. This brings a relatable perspective to the efficacy and practicality of the TendviaTM system. It reinforces that innovative devices can be successfully integrated into routine clinical practice, even in environments where resources or patient profiles may be challenging.
Consider the following bullet points summarizing the study’s real-world implications:
- Accessibility of advanced therapies: Medical centers worldwide can consider adopting these techniques, potentially leading to a standardization of care for high-risk pulmonary embolism.
- Enhanced interdisciplinary collaboration: Successful outcomes rely on the close cooperation of interventional cardiologists, cardiovascular surgeons, and intensive care specialists.
- Opportunity for further research: The promising results invite larger studies and multi-center trials, which are needed to refine procedural protocols and patient selection criteria.
The ability of this study to work through the tangled issues of clot management brings hope for a future where high-risk pulmonary embolism is no longer seen as an off-putting challenge. Instead, it is a condition for which practical, safe, and effective solutions are readily available.
Addressing the Concerns and the Fine Points of the Technique
As with all innovative medical procedures, there remain a few tricky parts and confusing bits that must be considered before widespread adoption of the TendviaTM system. While the study shows a promising safety profile and significant clinical improvements, a few areas deserve additional scrutiny:
- Patient Selection: The success of mechanical thrombectomy hinges on choosing the right patient. Those with contraindications to the procedure or who are too unstable may not be ideal candidates, and further research is needed to delineate these boundaries.
- Long-Term Outcomes: Although the short-term results are compelling, there is a need for longer follow-up periods to assess the durability of the clinical improvements.
- Operator Expertise: Like many percutaneous procedures, the effectiveness of the intervention is highly dependent on the skill of the operator. Training programs and standard operating procedures will be essential as more centers begin to use this technology.
- Cost and Resource Utilization: As healthcare systems across the globe work through financial constraints, the cost-effectiveness and resource allocation for such advanced techniques will need to be thoroughly evaluated.
These considerations are not meant to detract from the positive study outcomes, but rather to highlight that every innovative medical technique has its subtle details and hidden complexities. By acknowledging and addressing these concerns, the goal is to work towards a broader, more robust clinical adoption that stands the test of time.
Integrating Mechanical Thrombectomy into Holistic Cardiovascular Care
The application of mechanical thrombectomy should not be viewed in isolation. A comprehensive cardiovascular care program involves integrating multiple disciplines, from emergency medicine to long-term rehabilitative strategies. The TendviaTM system represents only one piece of the overall management puzzle. Here, it is important to figure a path that incorporates several elements:
- Preventive care: Recognizing the early signs of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and managing risk factors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and smoking is key to reducing the overall incidence of pulmonary embolism.
- Interdisciplinary cooperation: The success of advanced interventions often depends on strong collaboration between various specialists, including cardiologists, pulmonologists, and critical care physicians.
- Patient education: Informing patients about the signs and symptoms of pulmonary embolism, as well as the available treatment options, empowers them to seek timely care and comply with therapeutic recommendations.
Integrating these elements with the promising outcomes of mechanical thrombectomy can lead to better, more coordinated care. Clinicians can use this evidence to further refine treatment protocols, ensuring that every patient receives the best possible outcome in an often intimidating medical scenario.
Expert Opinions: Is Mechanical Thrombectomy the Future?
The ongoing debate about the future of pulmonary embolism management is both dynamic and exciting. Medical experts and opinion leaders have begun to get into discussions about whether mechanical thrombectomy procedures might gradually replace or complement thrombolysis as the primary treatment approach for high-risk patients. From an expert standpoint, the TendviaTM system offers several promising prospects:
- Immediate restoration of blood flow: In scenarios where every minute counts, rapid mechanical intervention could be the deciding factor between recovery and deterioration.
- Reduced risk of systemic bleeding: By circumventing the need for systemic thrombolytic agents, the risk of significant bleeding complications is reduced—one of the main concerns with traditional therapy.
- Potential for adaptive use: As the technology matures, we may see adaptations and improvements that further refine the system, making it even more effective and easier to deploy.
However, it remains clear that while mechanical thrombectomy is set to play a key role, it will most likely complement rather than completely replace conventional therapies. More extensive studies and real-world data are needed to confirm how this technique fares over longer periods and in diverse patient groups. The conversation is still evolving, and as practitioners continue to figure a path through these tricky parts, the future of pulmonary embolism treatment looks set to be radically transformed.
Long-Term Benefits and Quality of Life Improvements
Beyond the immediate clinical improvements in pulmonary artery pressure and heart function, the long-term advantages of using a system like TendviaTM are also worthy of discussion. Restoring blood flow promptly not only reduces the acute burden on the cardiovascular system but can also provide lasting benefits that extend to the overall quality of life for patients. Consider the following benefits:
- Improved exercise tolerance: As patients recover quicker, they can resume physical activity sooner, leading to better overall cardiovascular health.
- Lower hospital readmission rates: Effective clot clearance may translate into fewer episodes of recurring embolism, which is a key consideration in health economics.
- Psychological relief: The knowledge that a rapid and safe intervention is available can reduce patient anxiety, an often-overlooked twist when managing severe cardiac conditions.
- Enhanced rehabilitation potential: With reduced cardiac strain, patients may find it easier to engage in rehabilitative therapies, promoting a more comprehensive recovery process.
These points underscore the idea that advanced medical interventions are not just about immediate survival—they also play a critical role in setting the course for long-term well-being. When we look at the evidence, it becomes clear that innovative therapies like the TendviaTM system have the potential to redefine recovery trajectories for patients enduring high-risk pulmonary embolisms.
Key Takeaways for the Healthcare Community
After poking around the details of this study, a few key takeaways emerge that are super important for healthcare professionals:
- Innovation is essential: The introduction of the TendviaTM system is an example of how thinking outside traditional treatment paradigms can yield significant benefits.
- Clinical evidence matters: Real-world studies are crucial in validating new approaches, particularly when confronted with the little twist of emergency care for high-risk patients.
- Team-based approaches: Managing high-risk pulmonary embolism requires coordinated effort, from acute intervention to long-term follow-up, ensuring that each step is managed with care.
- Ongoing education: Keeping up with evolving treatment modalities is critical, as we all need to be adaptable in a field where the unexpected is often loaded with issues.
For clinicians, policymakers, and researchers alike, studies on devices like the TendviaTM system represent more than just a clinical trial—they symbolize a broader shift towards mechanical approaches that can tackle even the most daunting challenges head-on. It is through such insights that the entire cardiovascular community can continue to evolve and improve its practices.
Challenges Ahead and Future Directions
Despite the significant promise shown by the TendviaTM pulmonary artery stent thrombectomy system, there are still several open questions and areas where further research is needed. Some of the challenges include:
- Scaling up the evidence: A study of 15 patients provides a glimpse, but larger, multicenter trials are required to confirm these early findings and determine broader applicability.
- Refining patient screening: Identifying which patients benefit the most from PMT is crucial. Future work must focus on developing precise criteria that can account for the subtle differences among patient subgroups.
- Integrating with existing protocols: As new interventions are introduced, they should be seamlessly integrated into existing clinical guidelines to maximize safety and effectiveness.
- Cost-effectiveness analysis: In an age of rising healthcare costs, establishing the economic benefits of mechanical thrombectomy relative to conventional treatments will be key in driving adoption.
Thus, while the current data is promising, we must be cautious and realistic. The road ahead involves a lot of sorting out of fine details and working through the practical issues when scaling the solution for wider use. It may take some time to fully integrate such advanced therapies into everyday practice, but with persistence and collaboration, the end result will likely benefit a significant number of patients worldwide.
A Broader Vision for Cardiovascular Health
In a healthcare environment that is continually evolving, the advent of mechanical thrombectomy devices like the TendviaTM system inspires us to re-examine our current treatment paradigms. The fine points of cardiovascular care are not only about treating acute events but also about embracing a comprehensive vision for long-term heart health. This vision includes:
- Preventive strategies: Focusing on lifestyle modifications, early diagnosis, and vigilant management of risk factors is as important as immediate therapeutic interventions.
- Technological integration: Leveraging advanced imaging, individualized data tracking, and real-time monitoring can help clinicians figure a path through the many challenging bits of cardiovascular disease management.
- Patient-centered care: Engaging patients in their recovery journey by providing clear information about procedures and expected outcomes is a crucial component of modern treatment protocols.
- Collaborative research: Sharing data across institutions and countries can accelerate the development of best practices, with each new study adding a piece to the evolving puzzle.
As healthcare providers, we must remain committed to continuously improving our approaches. In doing so, we help ensure that even the most intimidating medical conditions are not met with hesitation but with a confident, evidence-based strategy that marries clinical excellence with compassionate care.
Conclusion: Charting a Course Toward an Optimized Future
The clinical evaluation of the TendviaTM pulmonary artery stent thrombectomy system offers an exciting glimpse into the future of pulmonary embolism management. With promising improvements in pulmonary artery pressure, right ventricular function, and patient symptoms, this study provides a solid foundation for future research and clinical application. While certain tricky parts and tangled issues remain, the results suggest that mechanical thrombectomy is set to become an essential tool in the treatment of intermediate-high and high-risk pulmonary embolism.
As we take a closer look at these developments, it becomes clear that innovative interventions are more than just an alternative—they are a means of pushing boundaries and redefining standard care practices. Whether you are a clinician, a researcher, or simply someone interested in the progress of modern cardiovascular medicine, this study should serve as a reminder that even in the face of daunting challenges, progress is always within reach.
Moving forward, further studies with larger patient populations and longer-term follow-up will be necessary to solidify the role of mechanical thrombectomy in cardiovascular care. It is through such endeavors that we can pave the way for more refined, safe, and effective treatment strategies. By combining this new approach with established medical practices, the healthcare community can confidently steer through the many turns and bumps of complex cardiac cases, ultimately improving outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for patients worldwide.
In summary, as we continue to figure a path through the ever-evolving landscape of cardiovascular therapy, the TendviaTM system stands as a beacon of innovation. Its demonstrated efficacy and safety profile offer hope for those facing life-threatening pulmonary embolism, and its future in mainstream clinical practice appears bright. With continued research, interdisciplinary cooperation, and a patient-centered approach, mechanical thrombectomy may well be one of the most significant advancements in cardiovascular medicine in recent years.
Originally Post From https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/cardiovascular-medicine/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2025.1685294/full
Read more about this topic at
Percutaneous Management of High-Risk Pulmonary …
Effective Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism and …


