Extended Half-Life FVIII Replacement in Pediatric Hemophilia: A Game-Changer?
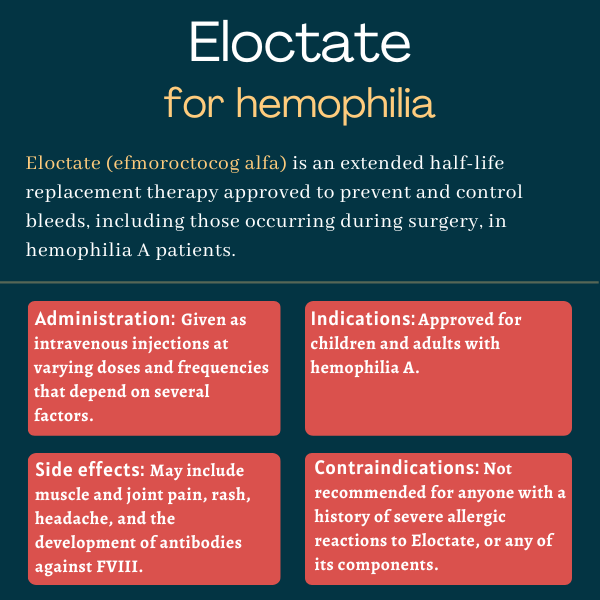
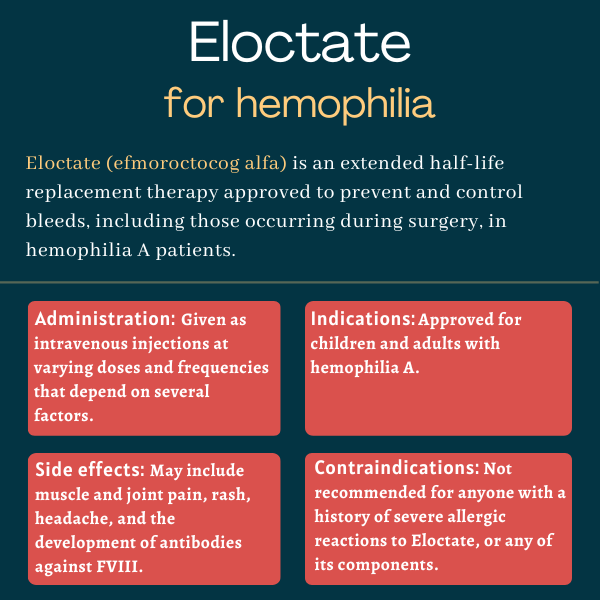
The treatment landscape for hemophilia A has seen significant evolution over the last few years. An exciting innovation in this space is efmoroctocog alfa, a treatment that provides extended half-life protection compared with standard factor VIII (FVIII) replacements. In recent studies – including one conducted in Turkey between 2024 and 2025 – the use of efmoroctocog alfa has shown promising results in reducing treatment burdens and enhancing bleed protection, particularly among pediatric patients.
At its core, this development offers a new approach in managing hemophilia A, a condition often characterized by repeated bleeding episodes and the need for frequent intravenous treatments. Traditional prophylactic regimens typically demand multiple weekly infusions, which can be overwhelming for patients and challenging to adhere to over time. By contrast, efmoroctocog alfa’s extended half-life feature could allow patients to receive fewer infusions, simplifying treatment plans, and potentially improving overall outcomes.
Reducing Treatment Burden with Extended Half-Life Solutions
Many healthcare providers are continually looking for ways to make treatment routines less nerve-racking for patients. One of the chief benefits of efmoroctocog alfa is the potential to reduce the number of infusions required, thus easing the treatment process. When compared with standard half-life products, this extended half-life option seems to address several of the tricky parts and tangled issues associated with traditional FVIII therapies.
Key Advantages for Children and Their Families
For pediatric patients and their caretakers, the management of hemophilia A represents a series of complicated pieces and overwhelming steps, not the least of which is the frequency of infusions. Consider these points:
- Fewer Infusions: Extended half-life translates to fewer intravenous administrations, thereby reducing the disruption to daily life.
- Enhanced Bleed Protection: Continuous infusion protocols with efmoroctocog alfa may yield steadier FVIII levels, which in turn minimizes bleeding episodes.
- Potential Cost-Efficiency: With fewer infusions required, there is a possibility for lower overall treatment costs over time, benefiting both patients and healthcare systems.
- Caregiver Relief: Less frequent dosing may reduce the anxiety and nerve-racking experience for caregivers who manage the daily routines of children with hemophilia.
These benefits collectively create an appealing profile for families striving to manage a condition that is often fraught with tension and ongoing medical challenges.
Clinical Experiences: Surgical Management with Efmoroctocog Alfa
In addition to its use as a prophylactic treatment, efmoroctocog alfa has been successfully implemented during various surgical interventions—a fact that adds a new dimension to its clinical utility. In the referenced study, efmoroctocog alfa was used not only in routine care but also in addressing routine surgical procedures such as dental extractions, circumcisions, and orthopedic fracture refixations.
Surgical Cases: Demonstrating Efficacy in Real-World Scenarios
Surgical management in hemophilia patients has always involved a high degree of caution due to the risk of excessive bleeding and complications. However, with efmoroctocog alfa, the results have been very promising. The study highlighted that:
- Surgical procedures were successfully managed without the occurrence of major bleeding episodes.
- No surgical complications were reported, even in cases that normally would be perceived as nerve-racking due to the inherent surgical risks.
- The continuous infusion method, delivering a steady state of FVIII activity, showcased the potential advantages of using extended half-life products in surgical settings.
These findings suggest that even when faced with the twists and turns of surgery, patients with hemophilia A might benefit substantially from efmoroctocog alfa’s robust performance during invasive procedures.
Understanding the Safety Profile: No Inhibitor Development in Untreated Patients
A key concern among healthcare providers is the risk of inhibitor development – where the body develops antibodies against the infused factor, rendering treatment less effective. The Turkish study involved both previously treated and untreated pediatric patients. Notably, none of the previously untreated patients developed inhibitors over the course of the study. This outcome is essential, as it provides additional assurance regarding the safe application of efmoroctocog alfa.
Comparing Safety Data: Efmoroctocog Alfa Versus Standard FVIII Products
The comparative safety profile is a central aspect, particularly when contrasted with standard half-life FVIII products. The study that got into the details of surgical cases, treatment adherence, and infusion frequencies provided additional insights. Consider the following points:
- Inhibitor Risk: None of the previously untreated (naïve) patients developed inhibitors, an important marker for reaping long-term benefits.
- Prophylactic Efficiency: Both primary and secondary prophylaxis with efmoroctocog alfa showed high treatment efficacy.
- Consistent Therapeutic Levels: The continuous infusion capability did not compromise the stability of FVIII activity levels, even during periods requiring rapid surgical intervention.
From a clinical perspective, ensuring that a product does not induce inhibitors is one of the most critical safety markers. The absence of inhibitor development in the study is a strong indication that efmoroctocog alfa may provide a safer alternative when compared with more traditional regimens.
Weighing the Pros and Cons in Hemophilia Management
No advanced therapeutic option comes without its set of challenges. While efmoroctocog alfa presents many advantages, it is important to take a closer look at both its strengths and areas where further study is needed. This reflective overview will help busy healthcare providers and caregivers figure a path through the decision-making process.
The Upside: Benefits that Address Common Treatment Woes
There is a variety of key benefits that make efmoroctocog alfa stand out:
- Extended Duration of Action: The extended half-life reduces the frequency of infusions, lessening the inconvenience and potential for missed doses.
- Flexibility in Prophylactic Dependency: With steady FVIII levels maintained during peak periods, patients are less likely to experience sudden or unexpected bleeding, even in scenarios that might be considered intimidating.
- Surgical Safety: Its performance during surgical interventions suggests that it can be safely used in a variety of surgical procedures, further reinforcing its clinical utility.
Challenges That Remain in the Landscape
Despite the strong points, there remain some confusing bits and subtle parts that need to be acknowledged:
- Limited Sample Size: With the study involving only 18 pediatric patients over one center, larger scale studies are needed to confirm the generalizability of the results.
- Data on Continuous Infusion: While initial results are promising, safety and efficacy data for continuous infusion methods still require further exploration, particularly across different age groups and clinical settings.
- Long-Term Outcomes: How efmoroctocog alfa performs over an extended period, especially regarding inhibitor development and overall bleed protection, calls for more comprehensive longitudinal studies.
This balanced view is essential. It is important that both clinicians and families understand that while efmoroctocog alfa might seem like an attractive option, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution without its own set of twists and turns.
Detailed Comparison: Efmoroctocog Alfa vs. Standard Half-Life FVIII Products
To put the discussion into a structured perspective, the following table provides a side-by-side comparison between efmoroctocog alfa and traditional FVIII products:
| Feature | Efmoroctocog Alfa (Extended Half-Life) | Standard FVIII Products |
|---|---|---|
| Infusion Frequency | Fewer infusions required | Multiple infusions per week |
| Bleed Protection | Consistent, prolonged FVIII levels | Fluctuating FVIII levels |
| Surgical Management | Successful management in dental, circumcision, orthopedic cases | Requires careful monitoring and adjustment |
| Inhibitor Development | No inhibitors noted in reported study cases | Risk present depending on patient history |
| Treatment Burden | Reduced overall treatment burden | Higher due to frequent dosing |
This table aims to provide a quick overview of the fundamental differences between the two treatment approaches. It is essential for healthcare providers to consider factors such as patient lifestyle, ease of administration, and overall risk of complications when making treatment decisions.
Addressing the Tricky Parts of Prophylactic Hemophilia Management
Modern hemophilia management is full of problems that require thoughtful approaches. Tailoring primary prophylaxis based on factors such as age, weight, bleeding frequency, and individual risk factors is super important. Many clinicians agree that while the promise of extended half-life treatments is exciting, the real-world implementation is sometimes loaded with issues that need careful navigation.
Individualized Treatment Protocols: Finding Your Way in a Complex Landscape
Every patient’s journey is unique, and developing a personalized prophylactic strategy is key to success. Healthcare providers need to:
- Assess Patient Needs: Evaluate the frequency of bleeding episodes, lifestyle factors, and the overall severity of the condition.
- Balance Safety and Convenience: Ensure that the planned regimen minimizes risks while offering the tangible benefits of less frequent dosing.
- Monitor Regularly: Engage in ongoing evaluation, including monitoring inhibitor development and overall safety during periods of treatment change or surgical intervention.
This individualized approach helps steer through the intertwined aspects of hemophilia care. It underlines the need to take a closer look at the fine points and hidden complexities of each case, making sure that the chosen treatment path is resilient to changes and unexpected challenges.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Hemophilia Treatment
While current findings regarding efmoroctocog alfa are promising, the journey is far from complete. Continued research, larger patient cohorts, and controlled clinical trials are necessary to confirm its long-term benefits and to resolve some of the remaining puzzles in hemophilia care. The future of treatment involves addressing several of the small distinctions and subtle details that make each patient’s experience unique.
Remaining Questions for Future Studies
Several important questions need to be answered as we work through the evolving landscape of hemophilia management:
- Long-Term Efficacy: How do patients fare over many years of treatment with efmoroctocog alfa in terms of bleed frequency and overall quality of life?
- Broader Patient Demographics: What outcomes might be expected when this treatment is applied to larger, more diverse populations across multiple centers and regions?
- Optimization of Surgical Protocols: Can further refinement in the continuous infusion method lead to even better surgical outcomes and reduced recovery times?
- Economic Considerations: How will extended half-life therapies impact the costs for healthcare systems and families, and what measures can be taken to optimize cost efficiency?
These issues remain areas ripe for exploration. As researchers poke around and get into the development of more advanced clinical protocols, there is a strong feeling that treatments like efmoroctocog alfa could stand as a blueprint for the next generation of hemophilia care.
Real-World Impact: Stories from the Frontlines
Beyond clinical trials and published studies, the real-world impact of any new therapy is best measured by the stories of patients, families, and clinicians. Anecdotal evidence suggests that when treatment protocols become less intimidating and complicated by reduced infusion frequencies, the overall experience improves markedly. Families report feeling less burdened by the nerve-racking regimen of weekly visits to infusion centers, and children can enjoy a more typical lifestyle, free from the constant disruption of multiple treatments.
Patient-Centered Outcomes: A Closer Look at Quality of Life
A comprehensive approach to hemophilia care must extend beyond laboratory values and surgical outcomes. Consider the following patient-centered benefits reported by families:
- Improved Daily Routines: With fewer treatment sessions, everyday activities such as school, sports, and social interactions are less likely to be interrupted.
- Greater Mental Well-Being: Reduced anxiety around bleeding episodes and the infrequent need for invasive procedures can lead to improved psychological health.
- Enhanced Family Dynamics: When treatment regimens are simplified, both patients and their caregivers have more time and energy to focus on life beyond the disease.
These factors contribute to a broadly improved quality of life that is as significant as the clinical improvements observed during treatment interventions. It’s these real-world improvements that often reinforce the value of adopting new therapies in clinical practice.
Integrating New Therapies into Existing Healthcare Systems
Even with promising clinical data, integrating a new treatment option like efmoroctocog alfa into existing healthcare systems can appear intimidating for providers and administrators. Key considerations include:
Streamlining Implementation Strategies for Better Outcomes
To ensure a smooth uptake of extended half-life treatments in real-world settings, healthcare systems may need to:
- Train Healthcare Professionals: Educate clinicians and nurses on the specific administration protocols and monitoring requirements for efmoroctocog alfa.
- Develop Clear Guidelines: Create comprehensive clinical pathways that address both prophylactic and surgical scenarios, helping providers figure a path through the more complicated pieces of care.
- Enhance Patient Education: Empower patients and families with clear, digestible information about the benefits and potential risks of the new therapy, so they can make informed decisions.
- Monitor and Report Outcomes: Establish robust data collection systems to continuously evaluate the impact of the new therapy, adjusting practices as needed based on feedback and real-world performance.
These implementation strategies are not only key to achieving clinical success with efmoroctocog alfa but also to ensuring that healthcare providers can manage the transitions and adjustments in treatment protocols smoothly.
A Broader Perspective: The Role of Innovation in Hemophilia Care
The introduction of efmoroctocog alfa is part of a broader trend toward innovation in the treatment of chronic diseases. Rather than simply addressing symptoms, modern therapies focus on fundamentally altering the disease process and improving long-term outcomes. In the case of hemophilia A, this means not only preventing bleeding episodes but also mitigating the psychological and social burdens that often accompany the condition.
Innovative Strategies: Evolving Beyond Traditional Treatments
The new wave of hemophilia treatments is characterized by a multi-faceted approach that includes:
- Genetic Therapies: Emerging gene therapies offer the potential for long-term correction of the underlying genetic factors causing hemophilia, although these are still in early developmental stages and come with their own set of challenges.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatment plans based on an individual’s unique biology and lifestyle factors is slowly becoming the norm, which means that options like efmoroctocog alfa can be integrated into a larger, patient-centered treatment paradigm.
- Technological Integration: Digital health tools and remote monitoring solutions are being used to track patient outcomes more effectively, ensuring that adjustments to treatment regimens can be made in real-time as needed.
In many ways, efmoroctocog alfa serves as an essential stepping stone on the journey toward more comprehensive and less disruptive care strategies for hemophilia A. As healthcare professionals work through the many subtle details and small distinctions between various treatment options, the goal remains clear: to improve patient outcomes while reducing the overall treatment burden.
Looking Forward: The Potential of Continuous Infusion Data
One of the intriguing facets of using efmoroctocog alfa is the potential for continuous infusion to further stabilize FVIII levels. This approach, while still in the early stages of data collection, shows tremendous promise in achieving consistent therapeutic levels that might minimize those sudden and unexpected dips that predispose patients to bleeding episodes.
Unpacking the Hidden Complexities of Continuous Infusion
While traditional intermittent infusions have been the standard for many years, the possibility of a continuous infusion regimen invites us to dig into the fine points of treatment delivery. In this context, the following considerations become especially important:
- Stability of FVIII Levels: Continuous infusion may reduce the fluctuations seen with intermittent dosing, helping to smooth out the peaks and valleys of FVIII activity.
- Patient Safety: More stable FVIII levels may translate into fewer episodes of major bleeding, which is an essential factor in reducing the ambiguous risks associated with surgical and non-surgical events.
- Ease of Administration: Although continuous infusion protocols require specialized equipment and careful monitoring, they offer another pathway for managing care with greater precision.
- Clinical Validation: Future studies will need to verify that continuous infusion not only maintains safe FVIII levels but also provides sustained bleed protection without introducing new risks.
Managing your way through these issues is a process that involves both clinical expertise and patient cooperation. As research digs into these matters further, it is anticipated that more clarity will emerge regarding the full potential of continuous infusion protocols when used with efmoroctocog alfa.
Implications for Healthcare Providers and Decision-Makers
The adoption of innovative therapies like efmoroctocog alfa presents important considerations for healthcare providers and policy decision-makers alike. The extended half-life offered by the treatment may result in a tangible reduction in the overall treatment burden, thus opening a conversation about resource allocation in public health systems.
Policy and Practice: Key Considerations for Widespread Adoption
Addressing the broader implications, several key elements deserve attention:
- Resource Optimization: With potentially fewer infusions needed, there is scope to decrease hospitalization times and reduce the cost burden on healthcare systems.
- Training and Education Programs: Ongoing education for both healthcare professionals and patients is essential to ensure that the transition to extended half-life treatments is as smooth as possible.
- Regulatory Oversight: As innovative therapies emerge, regulatory bodies must work hand in hand with clinical experts to establish robust guidelines that safeguard both efficacy and safety.
- Insurance Considerations: Payers will need to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of these therapies in the long term, taking into account not only direct treatment costs but also the potential savings associated with reduced hospital visits and improved patient quality of life.
These factors illustrate that while the clinical data supporting efmoroctocog alfa are promising, wider adoption in real-world practice depends on a concerted effort from multiple stakeholders. As practitioners figure a path through the small distinctions and tricky parts of integrating new treatments, the collaborative efforts of healthcare teams and insurance providers will be critical in achieving optimal outcomes.
Final Thoughts: Balancing Innovation with Practicality
As we take a closer look at the evolution of hemophilia A treatment, it becomes clear that efmoroctocog alfa represents one of the promising steps forward in reducing the everyday burden on patients and their families. While the extended half-life feature and its surgical applications make a strong case for its use, the healthcare community must work through the subtle parts of data interpretation, uphold patient safety, and thoughtfully plan for real-world applications.
The technology is still evolving, and more controlled, large-scale studies are required in order to confirm these initial findings. However, early results show that efmoroctocog alfa may not only replace some of the current standard therapies but may also pave the way for innovative treatment strategies that lessen the nerve-racking inconveniences associated with regular intravenous infusions.
Weighing the Benefits and Considerations
When tallying the practical advantages, one must remember the following:
- Extended protection provided by efmoroctocog alfa has the potential to reduce frequent clinical visits.
- The stable FVIII activity levels achieved with this treatment are essential for managing both routine care and surgical procedures.
- Individualized treatment strategies based on patient-specific needs are essential for maximizing the potential of innovative therapies.
- Ongoing research and experience will help healthcare providers figure a path through the confusing bits associated with the transition to new treatment protocols.
In this rapidly changing field of hemophilia management, every piece of data brings us closer to a more refined understanding of how to best support patients in their daily lives. As the research community continues to get into the little details and fine shades of treatment efficacy and safety, both patients and providers can look forward to a future that is less off-putting and more accommodating to the challenges of living with hemophilia.
Conclusion: A Step Toward a Brighter Future in Hemophilia Care
In summary, efmoroctocog alfa appears to hold significant promise as an extended half-life FVIII replacement therapy for pediatric patients with hemophilia A. Through its capacity to reduce infusion frequency and enhance bleed protection—even during surgical interventions—it addresses many of the tangled issues inherent in traditional treatment methods. While the journey is embedded with tricky parts, such as integrating continuous infusion data and overcoming the small sample sizes of initial studies, the early evidence is optimistic.
For patients and caregivers navigating the nerve-racking realm of hemophilia treatment, innovations like efmoroctocog alfa may soon translate into a less intimidating regime and a better quality of life. With further controlled and large-scale studies on the horizon, the full potential of extended half-life therapies will likely be revealed, allowing healthcare providers to craft more convenient, effective, and individualized treatment pathways.
Ultimately, while there remain plenty of twists and turns along the road to innovation, the promise of reducing treatment burdens and increasing surgical safety offers a beacon of hope in a field that has historically been challenging. By working collaboratively, investing in further research, and keeping patient perspectives at the forefront, the journey toward improved hemophilia care looks brighter than ever.
Originally Post From https://www.hematologyadvisor.com/news/efmoroctocog-alfa-hemophilia-reduce-treatment-burden-risk/
Read more about this topic at
Extended half-life factor IX prophylaxis up to every 21 days …
Nothing short of a revolution: Novel extended half-life factor …