Understanding the Challenges of Craniocervical Vascular Malformations
In recent years, the management of vascular malformations at the craniocervical junction has been on the forefront of neurosurgical innovation. This editorial takes a closer look at the evolving techniques that combine advanced imaging technology with minimally invasive procedures, focusing on the role of endoscope‐integrated indocyanine green (ICG) videoangiography for complex arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs) and anterior spinal artery aneurysms.
The treatment of craniocervical vascular issues is full of tricky parts and tangled issues. With the introduction of endoscopic methods integrated with ICG videoangiography, neurosurgeons have found a way to get into the fine details of minute vascular structures that were once elusive. In this editorial, we explore the benefits and challenges of these emerging technologies, share insights from a groundbreaking case report, and discuss how these methods can help us figure a path through the twists and turns of treating AVFs at the craniocervical junction.
Revolutionizing Neurosurgery with Endoscope-Integrated ICG Videoangiography
Innovative techniques in neurosurgery have always needed to strike a delicate balance between thorough evaluation and minimally invasive intervention. The integration of ICG videoangiography into endoscopic procedures has dramatically improved the precision with which surgeons can assess blood flow and the hidden complexities of vascular structures. This technique provides real-time, high-resolution imaging that is key when dealing with subtle parts of a lesion.
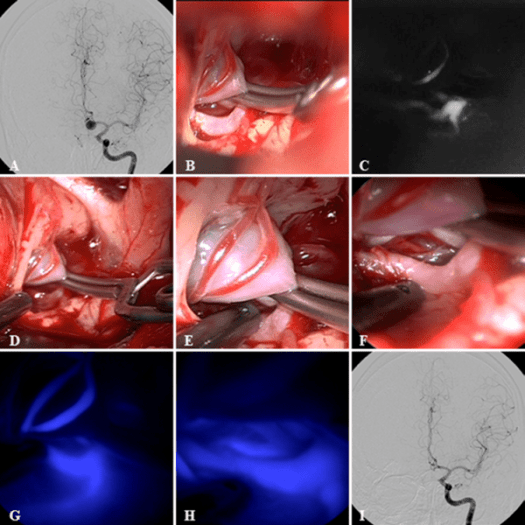
Using ICG videoangiography, the surgeon is able to dive in and get a closer look at the complex vascular network. The high-definition images reveal small, abnormal vessels that might be missed with traditional digital subtraction angiography (DSA) alone. In cases of epidural AVFs with anterior spinal artery aneurysms, this clarity can make the difference between a successful shunt interception and a procedure that falls short of completely stopping the aneurysm’s blood supply.
This innovative imaging method allows clinicians to see the little details of blood flow, ensuring that even the strangest, trickiest pieces of the vascular network are addressed. As our understanding of neurovascular anatomy evolves, the ability to assess these fine points with such precision is emerging as a super important development in the field. It is a key example of how modern medicine is working through challenging neurovascular conditions.
Case Report Insights: A Closer Look at a Trailblazing Procedure
One influential case that underscores the value of endoscope-integrated ICG videoangiography involved a 44-year-old man who presented with sudden symptoms including a severe headache and neurological deficits. The patient’s condition was complicated by a hematomyelia and, as subsequent imaging revealed, an epidural AVF with a concurrent anterior spinal artery aneurysm.
In this case, traditional DSA provided a broad understanding of the vascular malformation but failed to capture the fine details of the abnormal vessels. With the employment of an endoscope-integrated ICG system, surgeons could directly observe the twisted and intertwined small vessels that were contributing to residual blood flow. Even when DSA did not immediately show the remnant flow within the aneurysm, the endoscopic view revealed faint, lingering signals that were critical to ensuring complete shutdown of the abnormal shunt.
This case report emphasizes that even when faced with overwhelming challenges and nerve‐racking decisions in the operating room, advanced imaging techniques can offer essential, real-time feedback. This immediate insight enables surgeons to promptly adjust their approach and secure successful outcomes.
Advanced Imaging in Neurosurgery: Benefits and Considerations
Enhanced Visualization of Tiny Vessels
One of the standout benefits of using endoscope-integrated ICG videoangiography is its capacity to capture the minuscule and subtle parts of vascular lesions. Traditional imaging methods sometimes gloss over vessels that measure below 0.5 mm in diameter. However, this state-of-the-art system offers enhanced resolution, allowing neurosurgeons to view little twists of the vascular anatomy that are critical for proper treatment planning.
- Real-time feedback allows immediate adjustments during surgery.
- High frame-rate imaging (over 30 frames per second) captures fast blood flow dynamics.
- The endoscopic view offers angled perspectives, reducing the need for excessive retraction and minimizing tissue manipulation.
These advantages are more than just technical improvements—they often translate into better patient outcomes by reducing the risk of incomplete occlusion or rebleed from residual abnormal vessels.
Comparative Advantages Over Traditional DSA
While digital subtraction angiography has long been the gold standard in visualizing vascular structures, it does come with certain limitations. The primary drawback of DSA is its relative inability to render very small vessels due to lower frame-resolution rates, typically 3-6 frames per second. This can lead to gaps in visualization when it comes to capturing the full nitty-gritty of vascular flow.
In contrast, ICG videoangiography not only offers a much faster frame rate but also integrates endoscopic magnification that can bring hidden details into clear view. This is particularly beneficial when assessing whether minor shunt flows or residual vessels are present, ensuring that neurosurgeons can take an even closer look before concluding a procedure.
Despite its advantages, it’s important to note that no single technique is without its challenges. The use of ICG videoangiography requires specialized equipment and a thorough understanding of the imaging technology. Training and experience are key to harnessing the full potential of this method while avoiding pitfalls such as misinterpretation of subtle signals.
Digging Into the Twists and Turns of Vascular Anatomy
Understanding the Fine Points of Vascular Networks
Vascular malformations at the craniocervical junction are characterized by a tangled web of feeding arteries and draining veins. The same complexity that makes these lesions difficult to treat is also what makes them fascinating to study. The detailed images provided by ICG videoangiography allow physicians to get into the nitty-gritty of the vascular anatomy, revealing layers of twisted branches that might not be apparent with conventional imaging.
These small distinctions in blood flow patterns and vessel morphology are critical for devising an effective treatment strategy. For example, determining whether a direct aneurysm manipulation is feasible or if the focus should shift to shunt interception depends heavily on understanding these subtle details. In cases like the aforementioned report, the ability to see even a slight remaining flow within the aneurysm signal has significant implications for the surgical plan.
The Role of Angled Endoscopy in Revealing Hidden Details
One of the most striking features of endoscope-integrated ICG videoangiography is its use of angled scopes (such as 30° and 70°) to examine the ventral side of the spinal cord. Traditional microscopic views, while useful, often do not provide the necessary perspective to appreciate all the intricate pieces hidden in the recesses of the neurovascular landscape. With angled endoscopy, surgeons can literally take a different view, freeing them from the constraints of a direct line-of-sight under the microscope.
This approach not only minimizes excessive spinal cord retraction—thus reducing the risk of neurological injury—but also exposes abnormal vessels that exit in less accessible areas. The ability to adjust the viewing angle and zoom in enhances the overall precision of the intervention and allows for swift identification and management of residual arterial flows.
Managing Your Way Through Treatment Options in Neurovascular Cases
Shunt Interception vs. Direct Aneurysm Clipping
When treating cases involving AVFs and associated aneurysms, one of the key surgical decisions revolves around whether to directly manipulate the aneurysm or to opt for shunt interception. In many cases, a direct approach can be intimidating or even risky if the aneurysm is located unfavorably, such as in a subpial position. Instead, shunt interception can be deployed to reduce the hemodynamic stress on the aneurysm, thereby promoting its eventual obliteration.
This method relies on the subtle observation of blood flow changes post-interception. As seen in the case discussed, the endoscopic ICG videoangiography was pivotal in confirming that the abnormal vessels feeding the aneurysm had ceased exhibiting flow. While the DSA might have shown residual trace signals, the endoscopic feedback allowed surgeons to see the stagnating flow, indicating a successful outcome. It is a clear example of how real-time imaging can help physicians work through the tangled issues of vascular treatment.
- Direct aneurysm clipping can be risky when the lesion is deeply embedded.
- Shunt interception offers an indirect way to cut off the aneurysm’s blood supply.
- Real-time imaging ensures that even lingering flows are detected and addressed.
The Importance of Postoperative Verification
Achieving a promising intraoperative result is only part of the equation. Fortunately, modern imaging techniques allow for rigorous postoperative assessment. Follow-up MR imaging and repeat angiography play a critical role in confirming that the surgical interventions have completely abolished the shunt and aneurysm.
In the case report, the disappearance of the enhanced lesion on T1-weighted MR images over a few months served as a successful indicator of treatment efficacy. These follow-up protocols are not only useful for detecting potential complications but also provide a reassurance of the long-term viability of the treatment. It is a methodical approach that underscores the super important role of long-term monitoring in managing neurovascular disorders.
Real-World Implications: From the Operating Room to Patient Recovery
Improved Surgical Outcomes Through Advanced Imaging
The adoption of endoscope-integrated ICG videoangiography has significantly altered the landscape of neurosurgical procedures. By offering a window into the blood flow dynamics within complex vascular networks, the technology equips surgeons with the confidence to perform interventions with higher precision.
Improved visualization means that surgeons can minimize the risk of incomplete removal of abnormal vessels—a factor that previously contributed to rebleeds or residual aneurysm recurrence. In an era where patient safety and outcome optimization are paramount, such advancements are more than just technical upgrades; they are transformative tools that help save lives.
Beyond immediate surgical success, improved imaging techniques have a ripple effect on patient recovery. The ability to reliably intercept shunt flow minimizes invasive manipulations and reduces the incidence of complications such as ischemic infarctions or hemorrhagic events. Over time, these benefits compound, contributing to lower rates of reoperation and a faster return to normal life for patients.
Case-Based Reflections on Clinical Practice
Reflecting on the case presented, several practical lessons emerge. First, when facing a challenging neurovascular setup, it is crucial to utilize every available tool to understand the fine details at play. Second, these advanced imaging methods are not just about seeing better—they are about making more informed decisions that directly affect patient outcomes. Even a faint signal, once observed, can guide a change in surgical strategy, ensuring that no stone is left unturned.
Moreover, the collaboration between surgical teams, imaging specialists, and support staff becomes paramount as technology continues to evolve. Each additional layer of insight helps the multidisciplinary teams work through confusing bits and tangled issues more efficiently. Finally, following rigorous postoperative imaging protocols ensures that the initial success is not marred by later complications, providing a full circle of care that is essential in modern neurovascular treatment.
Digging Even Deeper: The Broader Impact on Neurosurgical Practices
The Evolution of Endoscopic Techniques in Spinal Surgery
The broader movement toward the integration of endoscopic techniques in spinal surgery is a testament to the ongoing evolution in the field. Traditional open surgeries, while effective, come with a myriad of risks such as tissue trauma and extended recovery times. Endoscopic systems, enhanced by ICG videoangiography, offer a less invasive alternative that can often yield the same—or even better—results when it comes to treating complicated vascular anomalies.
This shift toward minimally invasive procedures has been driven by the need to reduce operative risks while maximizing precision. By using advanced endoscopic views and real-time imaging feedback, surgeons can make informed decisions in a nerve‐racking operating environment, ultimately resulting in greater patient safety and improved outcomes. These techniques are particularly appealing when dealing with neurovascular malformations, which require a delicate touch and an unwavering focus on the subtle details of the vascular network.
Adapting to New Technologies: Training and Skill Development
The integration of advanced imaging in neurosurgery necessitates a corresponding evolution in surgical skills and training. Surgeons and operating room staff must be adept at using these new tools, which means investing time in training and simulation. Learning to interpret the high-frame-rate images and discerning between various flow patterns in real time requires both experience and a willingness to embrace new technology.
Institutions that prioritize continuous learning and skill development are better positioned to adopt these technologies with success. Workshops, peer-reviewed journals, and hands-on training sessions are all components of a robust educational curriculum aimed at ensuring that the benefits of advanced endoscopic technology translate into better patient care. As we see more centers adopting these techniques, collaborative efforts will play a pivotal role in refining best practices and standardizing protocols.
Key training points include:
- Interpreting high-resolution, real-time ICG videos.
- Understanding the physics behind light-based angiography.
- Managing the nuanced differences between various imaging modalities.
- Strategically planning interventions based on detailed vascular maps.
- Ensuring effective communication among multidisciplinary teams.
Addressing Concerns and Future Directions in Neurovascular Imaging
Overcoming Technological Limitations and Growing Pains
Every emerging technology comes with its own set of challenging bits. In the case of endoscope-integrated ICG videoangiography, one limitation is its current inability to detect lesions that are deeply buried within brain or spinal tissues. There can be situations where the imaging technique falls short when the lesion lies beyond superficial layers. However, as technology advances and imaging resolution improves, we are likely to see further refinements that can address these gaps.
Continuous research is essential in overcoming these limitations. Future advancements may lead to enhanced penetration depths or integrated multimodal imaging systems that combine the strengths of different technologies. The potential for artificial intelligence to aid in real-time image interpretation is another exciting avenue. Such innovations could help in recognizing subtle details, thereby making the surgery even safer and more precise.
Guiding Future Research in Neurovascular Management
The promise of endoscope-integrated ICG videoangiography extends far beyond the treatment of a single type of lesion. Its utility in mapping fine shades of blood flow dynamics suggests that it could be applied to a wide range of neurovascular disorders. Future research might focus on expanding its applications to other challenging conditions, including complex aneurysms in other parts of the brain, arteriovenous malformations, and various spinal vascular lesions.
Researchers and clinicians alike should consider collaborative studies that compare the outcomes of surgeries performed with and without this technology. Such studies could provide evidence for best practices and reveal areas where further improvements are necessary. A strong emphasis on multicenter trials will also help gather robust data, encouraging wider acceptance and integration of these advanced methods into standard practice.
In summary, future research should aim to:
- Validate the long-term outcomes of surgeries utilizing ICG videoangiography.
- Develop enhanced imaging systems with deeper tissue penetration.
- Integrate artificial intelligence for faster and more accurate image interpretation.
- Explore applications in other neurovascular conditions and complex surgical scenarios.
Practical Implications for Clinicians and Patients
Translating Technological Advances into Everyday Practice
The introduction of endoscope-integrated ICG videoangiography into the neurosurgical arena is a clear step forward in patient care. For clinicians, it represents a tool that can help steer through even the most confusing bits of vascular treatment. This technology provides a level of detail and real-time information that supports more confident intraoperative decisions.
From a practical standpoint, using such advanced imaging can reduce the need for repeat surgeries and lower the risk of complications. As the technology becomes more widespread, it is likely to become a standard part of the neurosurgical toolkit, especially in centers treating complex craniocervical vascular malformations.
In everyday practice, this means:
- Better visualization of the surgical field, reducing operative time.
- Enhanced confidence in achieving complete obliteration of malformations.
- More precise interventions that lead to quicker patient recovery.
- Reduced likelihood of reintervention due to missed residual blood flow.
For patients, the implications are equally positive. Less invasive procedures paired with precise imaging can substantially reduce recovery times and lower the risk of complications. Patients benefit from shorter hospital stays and more predictable long-term outcomes, making this technology a true game-changer in neurovascular surgery.
Empowering Patients Through Transparent Communication
One of the most valuable aspects of these advanced techniques is the potential for improved communication between clinicians and patients. With real-time imaging, surgeons can better explain the nature of the vascular problem and the steps taken during surgery to address it. This transparency helps demystify the procedure for patients, alleviating some of the overwhelming fears associated with brain and spinal surgeries.
Educational materials that incorporate images from ICG videoangiography can be especially helpful. They allow patients to visualize the procedure and understand how the technology improves surgical accuracy. Ultimately, this fosters trust and collaboration between the medical team and the patient, which is essential for the success of any treatment plan.
Concluding Thoughts: A Forward-Looking Perspective in Neurovascular Treatment
The integration of endoscope-integrated ICG videoangiography into neurosurgery represents a transformative development that simplifies the management of craniocervical vascular malformations. By providing a clear, real-time perspective on even the most tangled issues of vascular anatomy, this technology helps neurosurgeons find their way through challenging procedures with greater confidence and precision.
While the techniques and technology continue to evolve, the current achievements mark a significant milestone in the journey toward safer, more effective neurovascular treatments. As we work to adopt these advanced methods into everyday practice, ongoing research, teamwork, and training will be super important in driving continued success.
Ultimately, the story of endoscope-integrated ICG videoangiography is one that reminds us of the innovative spirit intrinsic to modern medicine. It is a reminder that by taking a closer look and embracing new technology, we can address even the most intimidating medical challenges with skill, clarity, and compassion—a crucial pathway toward a healthier future for all.
Originally Post From https://jmedicalcasereports.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13256-025-05575-7
Read more about this topic at
Enhancement of vascular visualization in laser speckle …
in vivo experiments with a vasculature filter